HbA1c: 5.2

What does an A1c level of 5.2 mean?
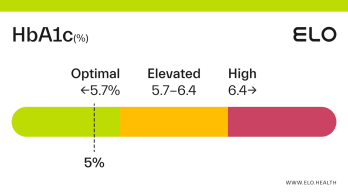
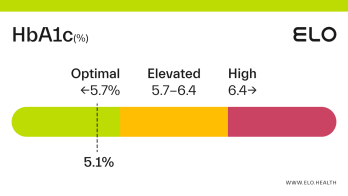
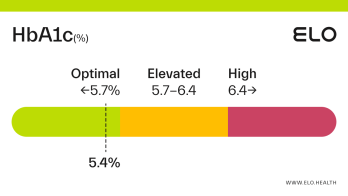
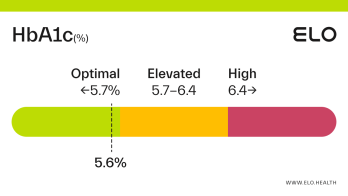
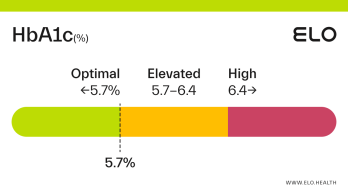
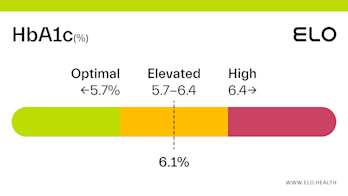
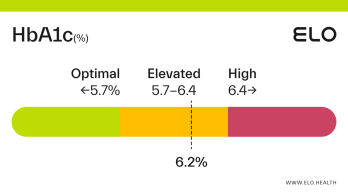
A hemoglobin A1c (aka HbA1c or A1c) level of 5.2 is considered optimal.
An A1c of 5.2 means that 5.2% of the hemoglobin in your blood is saturated with sugar. A1c levels between 4 and 5.6 percent indicate good blood glucose control over the last 2-3 months. Maintaining an optimal A1c is important for preventing diabetes and the complications associated with this diagnosis.
How to maintain optimal A1c levels
An A1c level of 5.2% means you have had good blood glucose control over the last few months. A1c often increases with age [4], so it’s important to have your levels checked on occasion, particularly if you’re at greater risk for developing prediabetes or diabetes.
Groups that are at greater risk for developing prediabetes/ diabetes include:
Adults age 45 or older
People of Black, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, Asian American, or Pacific Islander descent
Individuals with a parent, brother, or sister with diabetes
Those who are overweight or obese
People who are physically inactive
Individuals with low HDL (good) cholesterol and/or high triglycerides
Those with high blood pressure, or who take medicine for high blood pressure
Women who had diabetes during pregnancy or who have been diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Regardless of whether or not you’re at increased risk for prediabetes/ diabetes, having a healthy, balanced diet and lifestyle are key to maintaining optimal A1c levels. Here are some things you can do to keep your levels in the green:
Exercise 30-60 minutes most days of the week.
Fill half of your plate with non-starchy veggies at every meal, and incorporate a source of lean protein and plant-based fat to assist with blood sugar control.
Avoid refined carbohydrates and too much added sugar. Choose whole-grain carbs such as whole wheat bread/ pasta, quinoa, farro, and steel-cut oats, instead.
Lose excess weight if you are overweight or obese.
If you have diabetes, follow your diabetes treatment plan.
Minimize stress and get adequate sleep to help balance hormone levels that can affect blood sugar.