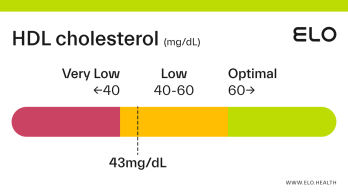
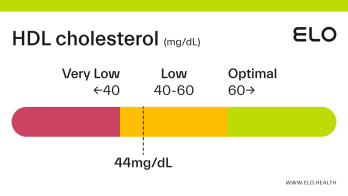
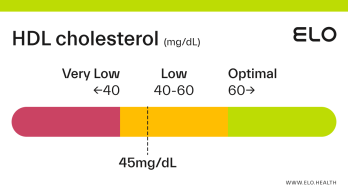
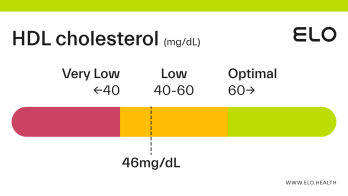
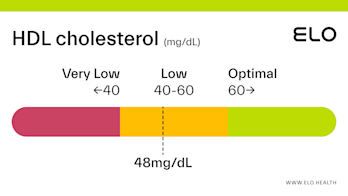
HDL Cholesterol: 48 mg/dL
What does an HDL level of 48 mean? Are there symptoms associated with this HDL level?
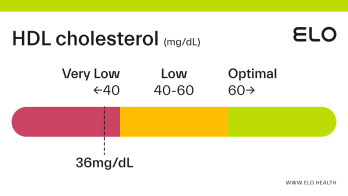
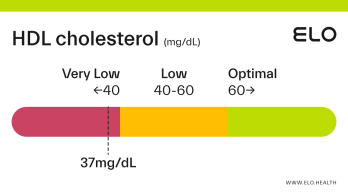
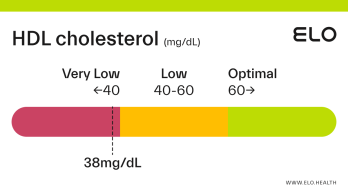
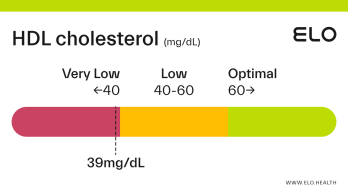
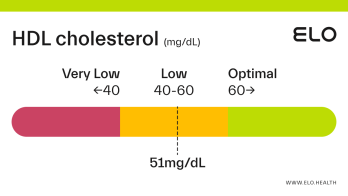
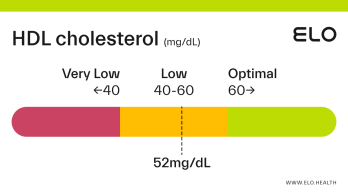
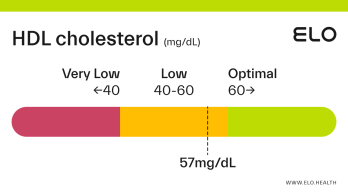
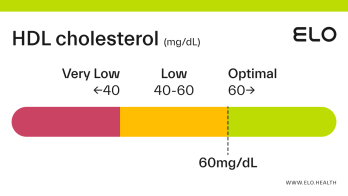
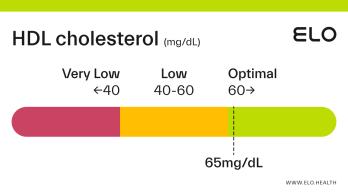
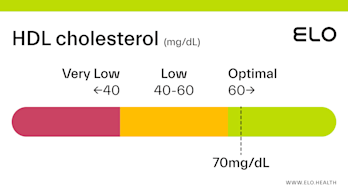
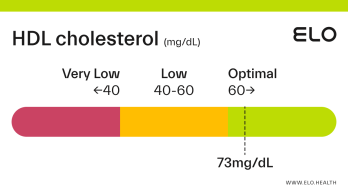
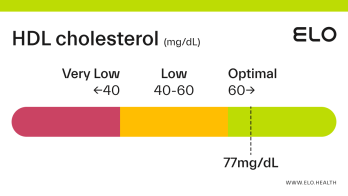
An HDL cholesterol level of 48 mg/dL is considered low. Levels >60 mg/dL are associated with a lower risk of heart disease, stroke, and heart attack.
Low HDL cholesterol doesn’t have symptoms, so it’s good to know your levels. Increasing your HDL cholesterol can help lower your LDL “bad” cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and reduce your risk of developing heart disease.
Factors that could contribute to an HDL level of 48
A variety of factors can affect HDL levels, including your diet, weight, activity level, age, sex, race, and genetics. Certain medications and diseases, as well as whether or not you smoke, also impact HDL levels.
Diet: Diets that are low in fiber and high in saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugar can lower HDL cholesterol.
Weight. Having excess fat, particularly around the abdomen, can also lower levels of HDL cholesterol.
Physical Activity. Being active can help increase HDL cholesterol levels and lower LDL.
Smoking. Smoking lowers your HDL cholesterol which can contribute to a higher level of bad cholesterol.
Medications: Some medications can lower HDL levels in some people. These include beta-blockers, anabolic steroids, progestins, and benzodiazepines .
Metabolic disease/ uncontrolled diabetes: Metabolic disease and uncontrolled diabetes can cause lower HDL levels.
Age and Sex: Women tend to have higher HDL levels than men, though levels usually decrease after menopause.
Genetics (heredity): Genetics play a role in cholesterol production, which is why family members commonly have similar levels. Though rare, very low HDL cholesterol levels can also be inherited. Medical conditions that severely lower HDL levels include Tangier’s disease and familial hypoalphalipoproteinemia.
Race. Hispanic Americans are more likely to have lower HDL levels, while Blacks/African Americans are more likely to have higher levels [8]. However, other risk factors, such as high blood pressure, obesity, or diabetes, may outweigh the health benefit of higher HDL levels.
Alcohol: Some evidence suggests moderate alcohol consumption may increase HDL levels [6]. For healthy adults, that means < 1 drink/day for women of all ages and men older than age 65, and < 2 drinks/day for men age 65 and younger [6].
What to do if your HDL level is 48?
If your HDL cholesterol level is 48 mg/dL, consult your doctor as they will need to evaluate your total cholesterol level to determine the best course of action. They may prescribe medication if your LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and triglycerides are high.
In the meantime, making changes to your diet and adopting healthier habits can help increase your HDL cholesterol level. Here are some things you can do to give your HDL a boost:
Aim to get 30-60 minutes of moderate physical activity 5x/week.
Eat more fiber, particularly from beans and whole grains, gradually increasing your fiber intake to 30-40 g/day.
Avoid trans fats, like hydrogenated oils, and limit saturated fats.
Eat small, fatty fish at least twice a week, including sardines, salmon, and mackerel.
Lose excess weight if you are overweight or obese.
Quit smoking.
Manage stress and get adequate sleep. Stress increases inflammation that can lower HDL.
Medications and supplements used to improve HDL results
Medications
Medications are not typically prescribed for low HDL levels unless LDL (bad) and triglycerides are elevated. This is because most cholesterol drugs target LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. HDL levels may increase as a result of taking these medications, however.
Fibrates: Help lower high triglyceride levels but may also help raise your HDL cholesterol.
Statins: Statins (including atorvastatin, simvastatin, and rosuvastatin) reduce cholesterol production in your liver and lower blood cholesterol. Because they typically need to be taken for life, statins are typically only prescribed if diet and lifestyle changes aren’t enough [3].
Supplements
Niacin: Niacin is a B vitamin that, when taken at prescription doses, can block the enzyme responsible for making cholesterol in the liver. Niacin therapy can also improve HDL levels and lower triglyceride levels, although it does not appear to reduce heart disease events, like heart attacks or strokes [9].
(Algal) omega-3: Made from certain marine algae, DHA-rich algal oil might help increase HDL cholesterol while lowering triglycerides, though it also seems to increase LDL (bad) cholesterol [10]. If your LDL cholesterol level is elevated, talk to your doctor before taking an algal omega-3 supplement.
Turmeric: A spice commonly used to flavor and color curry dishes, turmeric may help increase HDL and lower pro-inflammatory markers, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides [11]. More research is needed to determine optimal form and dosage but supplementing with 500 mg/day appears safe and potentially beneficial cholesterol.
References
Cholesterol Levels: What You Need to Know. (n.d.). U.S. National Library of Medicine | NIH. Retrieved September 9, 2021, from
https://medlineplus.gov/cholesterollevelswhatyouneedtoknow.html
Carotid Artery Disease. (n.d.). National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute | NIH. Retrieved September 9, 2021, from
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/carotid-artery-disease
High cholesterol. (n.d.). NHS Inform. Retrieved September 9, 2021, from
https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/blood-and-lymph/high-cholesterol
Racette, S. B., Lin, X., Lefevre, M., Spearie, C. A., Most, M. M., Ma, L., & Ostlund, R. E., Jr (2010). Dose effects of dietary phytosterols on cholesterol metabolism: a controlled feeding study. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 91(1), 32–38.
https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.28070
Cholesterol: Types, Tests, Treatments, Prevention. (2020, July 31). Cleveland Clinic.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/11920-cholesterol-numbers-what-do-they-mean
HDL cholesterol: How to boost your “good” cholesterol. (2020, November 10). Mayo Clinic.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/in-depth/hdl-cholesterol/art-20046388
HDL: The “Good” Cholesterol. (2019, April 18). National Institutes of Health.
https://medlineplus.gov/hdlthegoodcholesterol.html
Blood Cholesterol | NHLBI, NIH. (2021, January 4). National Institutes of Health.
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/blood-cholesterol
Schandelmaier, S., Briel, M., Saccilotto, R., Olu, K. K., Arpagaus, A., Hemkens, L. G., & Nordmann, A. J. (2017). Niacin for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular events. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 6(6), CD009744.
https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009744.pub2
Bernstein, A. M., Ding, E. L., Willett, W. C., & Rimm, E. B. (2012). A meta-analysis shows that docosahexaenoic acid from algal oil reduces serum triglycerides and increases HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol in persons without coronary heart disease. The Journal of nutrition, 142(1), 99–104.
https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.148973
Qin, S., Huang, L., Gong, J., Shen, S., Huang, J., Ren, H., & Hu, H. (2017). Efficacy and safety of turmeric and curcumin in lowering blood lipid levels in patients with cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition Journal, 16(1), 68.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-017-0293-y